Mar 19, 2024 | Events, Scholarly publishing
 On Tuesday 12th March we headed off to one of the industry’s leading events in academic publishing. This year the London Book Fair was buzzing; the main hall was filling up as soon as the doors opened, and the Tech Theatre and Main Stages had consistent queues. Meetings, networking and seminars are all key elements of the fair and this year we were lucky enough to participate and find out more about the challenges facing the industry.
On Tuesday 12th March we headed off to one of the industry’s leading events in academic publishing. This year the London Book Fair was buzzing; the main hall was filling up as soon as the doors opened, and the Tech Theatre and Main Stages had consistent queues. Meetings, networking and seminars are all key elements of the fair and this year we were lucky enough to participate and find out more about the challenges facing the industry.
The hot topic as ever was AI, and we attended a talk hosted by Sureshkumar Parandhaman (AVP of Publishing Solutions and Pre-Sales, Integra) entitled “Embracing AI in Publishing: Transform Editorial Excellence and Enhance Downstream Efficiency”. Needless to say it’s evident that tools are being developed to tackle many of the administrative tasks that editorial services provide, however we know there will still be an important role for us to play as integrity, quality and efficiency are all integral within our roles.
During a key discussion about AI and copyright it was stated that when King Charles’ recent surgery was announced, over 250 AI-generated texts filled the virtual Amazon bookshelves the very next day! Content is quick to make, and the session “Global Discussion of Machines, Humans, and the Law” hosted by Glenn Rollans (President and Publisher, Brush Education Inc.), Nicola Solomon (CEO, Society of Authors), Porter Anderson (Editor-in-Chief, Publishing Perspectives), Dan Conway (CEO, The Publishers Association UK) and Maria A. Pallante (President and CEO, Association of American Publishers) highlighted how important it is for the copyright holder to be accredited and financially rewarded. Whilst Government bodies manage policy and next steps with regards to AI, we need to be mindful of what we “feed” to LLMs and how “Fair Use” comes into play.

The Editorial Hub at LBF 2024
A panel discussion entitled “AI & Publishing – Navigating the Impact of Large Language Models” was hosted by Lucy McCarraher (Founder, Rethink Press Limited), Nadim Sadek (Founder & CEO, Shimmr AI Ltd), and Sara Lloyd (Group Communications Director & Global AI Lead, Pan Macmillan). The group discussed the ways that LLMs can spark creative thinking and should be used within workshops as a tool to support creativity. In terms of optimising the features of AI it was recommended that the industry looks to use it for creating the structural analysis needed for promotion work. An AI bot can extract book DNA far quicker than a pair of human eyes, so let’s use its skillset appropriately and it can enhance our work, rather than hinder progress. As well as creating copy, it can also be useful for generating advertising and images. As well as connecting couriers and customers, it can scroll databases to highlight potential consumers. The panel really encouraged the audience to engage with the features of AI bots and embrace how useful it can be to enhance and build on capabilities.
Feb 6, 2024 | Scholarly publishing
The ALPSP panel for this discussion on AI and the impact it is having within academic publishing was made up of Nicola Davies, IOP Publishing (Co-chair), Helene Stewart, Clarivate (Co-Chair), Meurig Gallagher, University of Birmingham (Speaker), Matt Hodgkinson, UKRIO (Speaker) and Jennifer Wright, CUP RI Manager (Speaker).
It was fascinating to see how the conversation around AI has moved on within a few months regarding this technological advancement. Institutions, publishers and journal stakeholders all have a concept of AI and are developing policies and guidance about how we should be using it and are underpinning the “what for?”.
Many of us by now will have tried asking a Large Language Model (LLM) to write a paragraph or create an image using Artificial Intelligence. It’s brilliant to watch how quickly tasks can be created, large blocks of text are generated at an immense speed, and right before us we see how quickly human intelligence can be mimicked. This notion was highlighted in Meurig Gallagher’s presentation; that essentially AI is trying to act as human as possible using the instructions it has been provided with. However, when these tools are posed with mathematical equations it does not have the knowledge to apply the learning and therefore can spectacularly fail! These “gaps” therefore build into the guidance stakeholders need to be aware of when creating policy around AI – it cannot be relied upon solely to do the work. Matt Hodgkinson developed this further and shared many caveats that researchers and general users might come up against when using chatbots:
- Many LLMs are unvalidated for scholarly uses.
- References should be fact-checked as they can be falsified, therefore it is important to check sources and supporting literature.
- The quality of evidence is not assured.
- Outputs may be based on using out-of-date information based on “old” training material.
The ominous but noteworthy warning was circulated that “if you are not an expert, you will be fooled by fluent but incorrect outputs”. Therefore, all of us involved in scholarly publishing need to be mindful of these contributions and check author statements within articles to assess whether an LLM has been used. Of course, one of the largest threats we are witnessing is the output of paper mills and their use of AI could lead to the tool’s collapse as its knowledge bank is infiltrated with “fake” data, which if left undetected will pollute the pool where the data is extracted from.
Nonetheless the principles of Research Integrity can be applied to the use of AI-generated content and Matt shared this slide to disclose how these principles are applied:
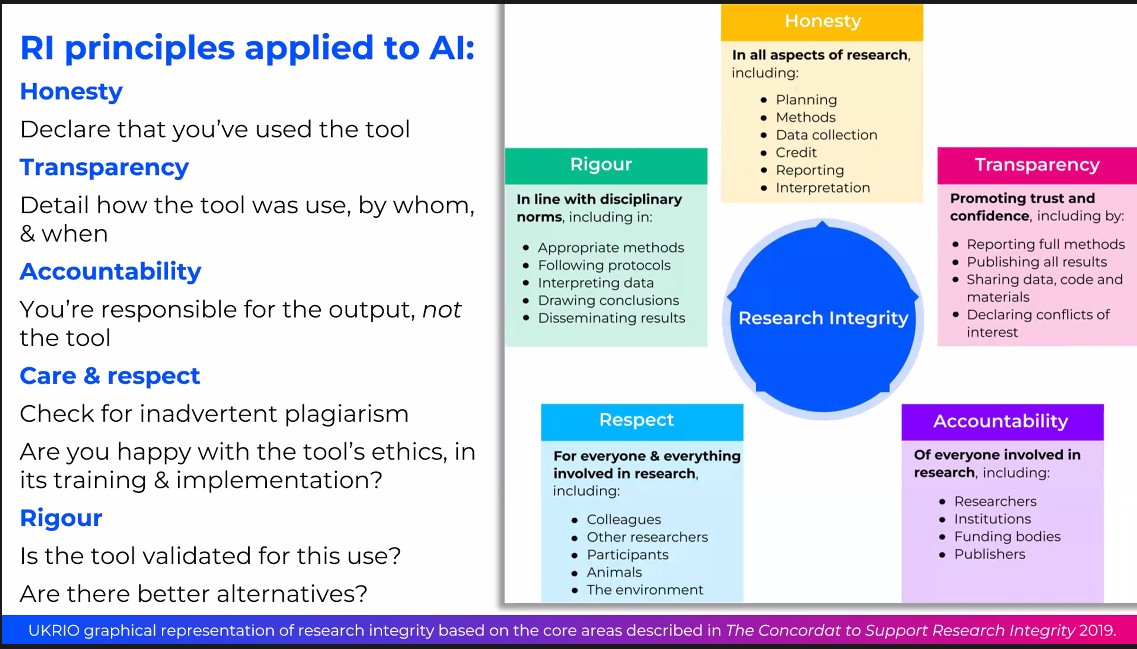
UKRIO presentation at ALPSP 2024
Dr Jennifer Wright from Cambridge University Press shared with the audience how to implement transparency which is really the crux of what many VEOs are looking at. It was suggested that AI declarations should be included within image captions, acknowledgements, and methodologies if applicable and the details that should be shared include the type of model that was used, eg: CHATGPT, and how and when it was accessed. It is also important to include any additional COI statements because of the use of the model. Looking forwards, Dr Wright elaborated on future considerations and posed some important questions around reporting standards: What will the impact be of AI on the scholarly record? How could/should/will research and publication practices change? How will concepts such as retractions be enforced? Can a bot retrain itself?
The challenges are still clearly evident with AI. However the more we progress and understand how it can be used, trust markers can be identified to validate the outputs. As long as scholars use and do not abuse the tech, we could watch something incredible unfold!
Dec 2, 2023 | Scholarly publishing
AI is inevitably going to infiltrate all our lives in some way or another in the near future; learning how we shop, communicate, write, create and plan our lives. We therefore also need to look at adapting our ways of working to benefit from these technological advancements. Working alongside this adaptive new tech, and generating new guidance and principles, will enable us to harness and nurture it. We can create preventative methods to stop bad actors abusing and infiltrating the systems we have in place to educate and teach.
At the NEC Annual Publishing Conference (7 November 2023, London), the keynote was delivered by David Smith from the IET who looked “Back to the Future!”; highlighting the importance of an article published by Darcy DiNucci. Fragmented Futures (published in print, 53.4, 1999) demonstrates technological growth and that the Web she wrote about was only the beginning…how things have changed in 20 years! Essentially it is thought we are at a similar point with AI; it is new, raw and ready to be refined and developed.
Leslie Lansmann, Global Permissions Manager from Springer Nature, discussed how Large Language Models (LLM) such as ChatGPT are ingesting content, and this is not yet fully disclosed by AI companies. This is important to monitor as we must maintain the stewardship for the content and protect copyright and protected manuscripts. As much as AI is currently learning – it probes and reiterates content – it does not understand the deeper context behind the language. The publishing industry is however having to react to the developments in technologies, many publishers are imposing bans on AI content, and introducing new and different policies.
The discussion around authorship is constantly developing and debated – should research be done using AI? Can it help an author whose first language isn’t English produce a more succinct piece of work? If the data is accurate and the same research principles are adhered to, maybe we should move towards incorporating it into our practices. This notion was delivered by Anastasia Toynbee from the Royal Society of Chemistry who was looking at the problem of non-native English speakers and how these tools could help. The key feature of this was that a problem had been highlighted and AI was being used to support it – not the other way around.
It became clear from all the speakers how important it is to identify the problem initially and use AI tech/tools to help with it, rather than decide how to harness and squeeze new systems into processes that are working well. Ian Mulvany at BMJ really brought home this idea that we as an industry need to balance risk vs opportunity. AI has perception, however no intention to act; therefore we are in a position through governance, policy, and stewardship that we can lead AI to improve processes and not be reactive and in fear of the unknown! Andy Halliday , Product Manager at F100 iterated the benefits and pitfalls of AI and how humans can help harness this tech and enable it to support our ecosystem and develop a sense of AI preparedness.
We are in the awakening of AI. The box has been opened and we all have access to create new and exciting content, images and access information much easier than ever before. As the discussions continue it will be really exciting to see how developments are made, what fixes it can be used for, and how policy and guidance are updated to meet the demands of users.
 On Tuesday 12th March we headed off to one of the industry’s leading events in academic publishing. This year the London Book Fair was buzzing; the main hall was filling up as soon as the doors opened, and the Tech Theatre and Main Stages had consistent queues. Meetings, networking and seminars are all key elements of the fair and this year we were lucky enough to participate and find out more about the challenges facing the industry.
On Tuesday 12th March we headed off to one of the industry’s leading events in academic publishing. This year the London Book Fair was buzzing; the main hall was filling up as soon as the doors opened, and the Tech Theatre and Main Stages had consistent queues. Meetings, networking and seminars are all key elements of the fair and this year we were lucky enough to participate and find out more about the challenges facing the industry. 




